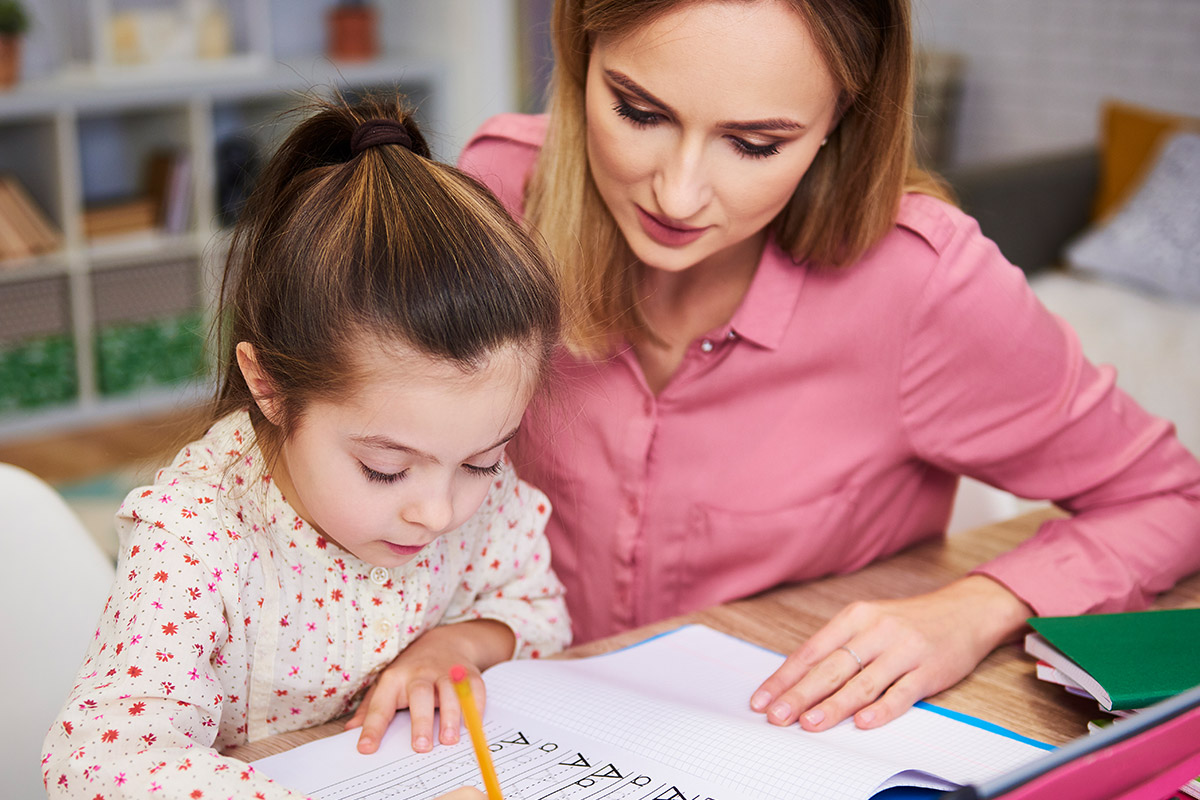
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become one of the most transformative technologies
of the 21st century, reshaping industries, enhancing everyday life, and
sparking both excitement and apprehension. However, despite its ubiquitous
presence, AI remains a complex and often misunderstood field. This blog aims to
demystify AI by explaining its basics, exploring its various applications, and
looking beyond the surface to understand its broader implications.
What is AI?
At its core, artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using the rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. AI can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Narrow AI: Also known as weak AI, this type of AI is designed and trained for a specific task. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, recommendation systems on Netflix and Amazon, and autonomous vehicles. Narrow AI systems can outperform humans in their specific domains but lack general intelligence.
- General AI: Also known as strong AI or artificial general intelligence (AGI), this type of AI possesses the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a broad range of tasks at a level comparable to human intelligence. AGI remains theoretical and has not yet been achieved.
Key Concepts in AI
To understand AI, it’s essential to grasp several foundational concepts:
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI, machine learning involves training algorithms to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. ML models improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of machine learning, deep learning uses neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to analyze various factors of data. This approach has driven advancements in image and speech recognition.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This field of AI focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. It involves enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Robotics: An interdisciplinary field within AI, robotics involves the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. AI-driven robots can perform tasks autonomously, often in environments where human presence is hazardous.
Applications of AI
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, AI poses several challenges and ethical dilemmas that need to be addressed:
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate and amplify biases present in their training data. Ensuring fairness and reducing bias in AI models is critical to prevent discrimination and ensure equitable outcomes.
- Privacy: The use of AI often involves processing vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security. It is essential to implement robust data protection measures and comply with privacy regulations.
- Transparency and Explainability: Many AI systems, particularly deep learning models, operate as “black boxes” with decision-making processes that are not easily understood. Enhancing transparency and explainability is crucial for building trust and ensuring accountability.
- Job Displacement: The automation of tasks through AI can lead to job displacement and economic disruption. While AI can create new job opportunities, there is a need for policies and initiatives to support workforce reskilling and transition.
Control and Safety: Ensuring that AI systems operate safely and as intended is paramount, particularly for applications like autonomous vehicles and healthcare. Establishing rigorous testing and validation processes is essential to mitigate risks.


Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, AI poses several challenges and ethical dilemmas that need to be addressed:
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate and amplify biases present in their training data. Ensuring fairness and reducing bias in AI models is critical to prevent discrimination and ensure equitable outcomes.
- Privacy: The use of AI often involves processing vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security. It is essential to implement robust data protection measures and comply with privacy regulations.
- Transparency and Explainability: Many AI systems, particularly deep learning models, operate as “black boxes” with decision-making processes that are not easily understood. Enhancing transparency and explainability is crucial for building trust and ensuring accountability.
- Job Displacement: The automation of tasks through AI can lead to job displacement and economic disruption. While AI can create new job opportunities, there is a need for policies and initiatives to support workforce reskilling and transition.
Control and Safety: Ensuring that AI systems operate safely and as intended is paramount, particularly for applications like autonomous vehicles and healthcare. Establishing rigorous testing and validation processes is essential to mitigate risks.
Intrinsic Motivation
Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum. Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium totam rem aperiam.
- Aute irure dolor in reprehenderit.
- Occaecat cupidatat non proident sunt in culpa.
- Pariatur enim ipsam.